On October 16, the 2024 Second China Offshore Photovoltaic Conference, organized by Solarbe Global, took place in Fuzhou. Dr. Liu Songmin, Executive Deputy Director of the Grand Sunergy New Energy Research Institute, was invited to present and delivered an engaging talk on Progress in Cost Reduction and Efficiency Improvement of HJT Mass Production and Offshore Applications.

Clear Path for Cost Reduction and Efficiency Improvement in HJT Technology
Dr. Liu began by outlining Grand Sunergy’s strategies for large-scale mass production of HJT technology, focusing on cost reduction and efficiency enhancement while discussing the current state of offshore photovoltaic development. He highlighted that silicon wafers and paste make up over 64% of the cost structure in HJT cells, noting that reducing costs associated with silicon and silver remains a major challenge for all crystalline silicon technologies, including PERC and TOPCon.

The advantages of HJT technology lie in its low-temperature processing and streamlined manufacturing, making it inherently favorable for thin silicon wafers, cost-effective silicon materials, and the substitution of silver with less expensive alternatives.
As the industry continues to innovate with specialized HJT silicon wafers, silver-copper pastes, 0BB technology, steel printing, and indium-free targets, HJT production costs are expected to decrease by around 0.188 RMB/W. Additionally, new technologies like steel plate printing, ACP textured surfaces, back polishing of silicon wafers, and high-mobility target materials could potentially improve mass production efficiency by approximately 0.55%.
Exceptional Adaptability to Complex Marine Environments
In addressing the unique demands of offshore photovoltaic systems, Dr. Liu introduced Grand Sunergy’s packaging solution for offshore photovoltaic modules, designed to deliver enhanced system value.
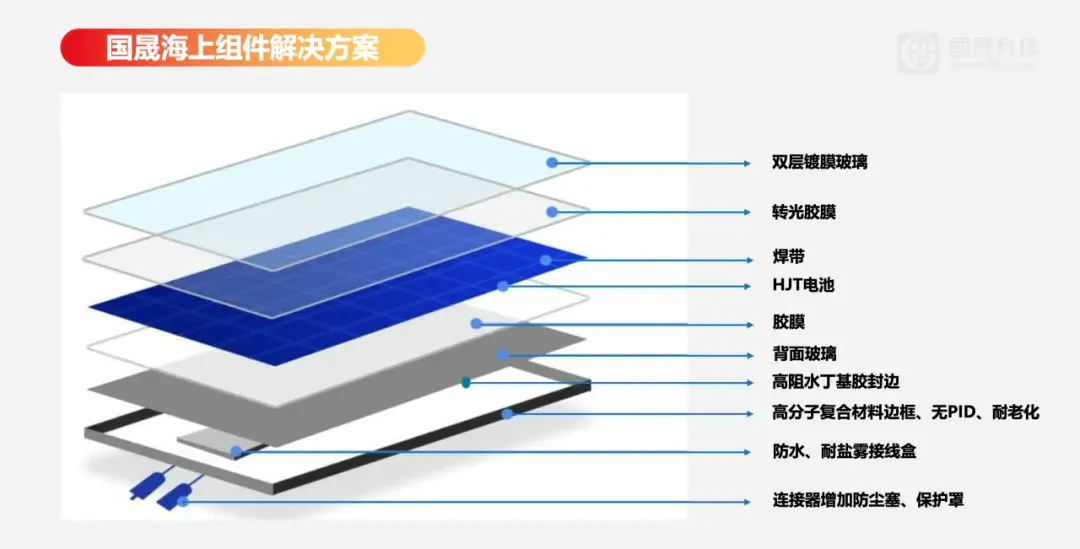
In the packaging process, photovoltaic glass primarily protects the cells, but its surface is vulnerable to corrosion from high-salinity marine environments. This can lead to salt crystallization and white spots, diminishing light transmittance and accelerating the PID effect, ultimately resulting in power loss. The Seapower HJT offshore module is equipped with a dual-layer dense SiO2 coating on the standard 2.0mm tempered glass, significantly improving resistance to salt mist and corrosion while enhancing water-repelling properties.
The encapsulant also faces challenges due to high ultraviolet radiation, water vapor, salt mist, and extreme temperature fluctuations, which threaten the reliability of photovoltaic cells. The light-converting encapsulant transforms UV light below 380nm into blue light in the 400-550nm range, significantly boosting the UV resistance of the HJT module. Additionally, the Seapower module features a high-water-resistant butyl edge sealing process, reducing moisture permeability by 99.9% compared to industry standards and effectively preventing moisture intrusion, further mitigating cell degradation.
The marine environment presents challenges like seawater corrosion, salt mist, and wave impacts that can compromise the system’s operational safety. The Seapower module uses a polyurethane polymer composite frame, measuring 35mm in thickness with a 2.0mm wall thickness, which offers exceptional weather resistance, high mechanical performance, and load-bearing capacity to withstand the forces of sea winds and waves. Remarkably, in aspects like deformation, misalignment, curvature, and tensile strength, the composite frame outperforms traditional aluminum frames.
HJT Modules Provide Enhanced System Value
Regarding the stability, reliability, and cost-effectiveness of photovoltaic systems, Dr. Liu pointed out that HJT technology combines high efficiency, reliability, substantial value, and low carbon emissions. It has shown impressive bifacial energy yield enhancements in both lab and outdoor settings.
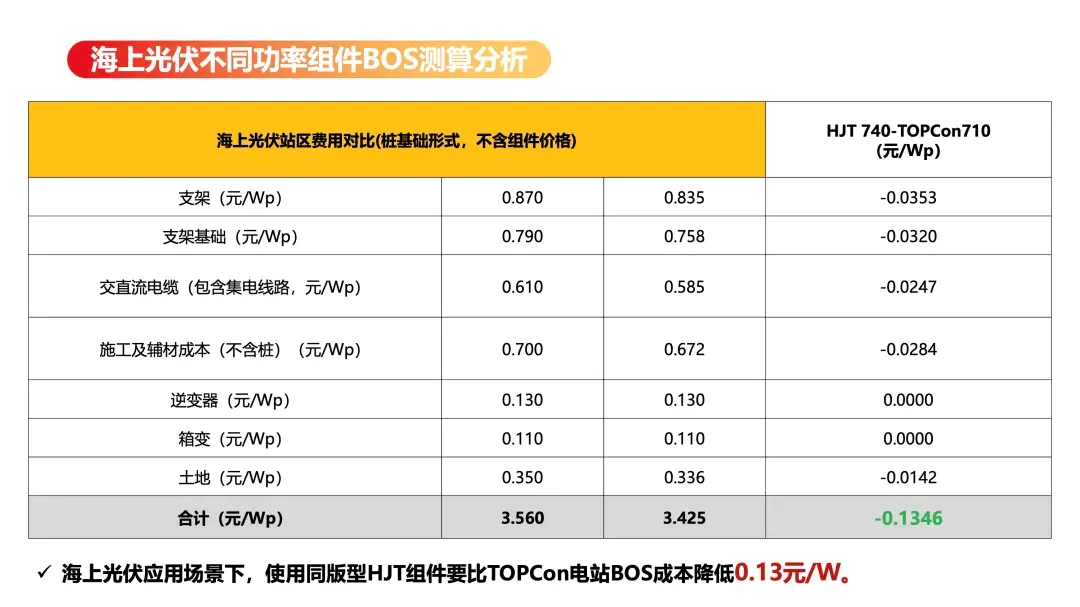
In terms of system value, the 740W-HJT-210 module can achieve a power increase of up to 30W and a 0.96% efficiency enhancement compared to similar TOPCon modules. With identical AC/DC installed capacity, it effectively reduces the number of photovoltaic modules, strings, mounts, and foundations required, decreasing the need for DC cabling and land usage, ultimately lowering construction, material, and labor costs. Based on estimates, Grand Sunergy’s Seapower modules can reduce BOS costs by around 0.1346 RMB/W compared to equivalent TOPCon models.
Grand Sunergy has successfully supplied efficient photovoltaic products for the 400MW offshore project in Zhaoyuan , China, as well as the 600MW salt-light complementary project in Laizhou, China. Looking ahead, the company will continue to customize the photovoltaics+ approach for various applications, driving technological innovations to enhance cost-effectiveness and contribute Grand Sunergy’s expertise through leading HJT photovoltaic technologies and solutions.

